Consequences to vessels
Consequences to vessels
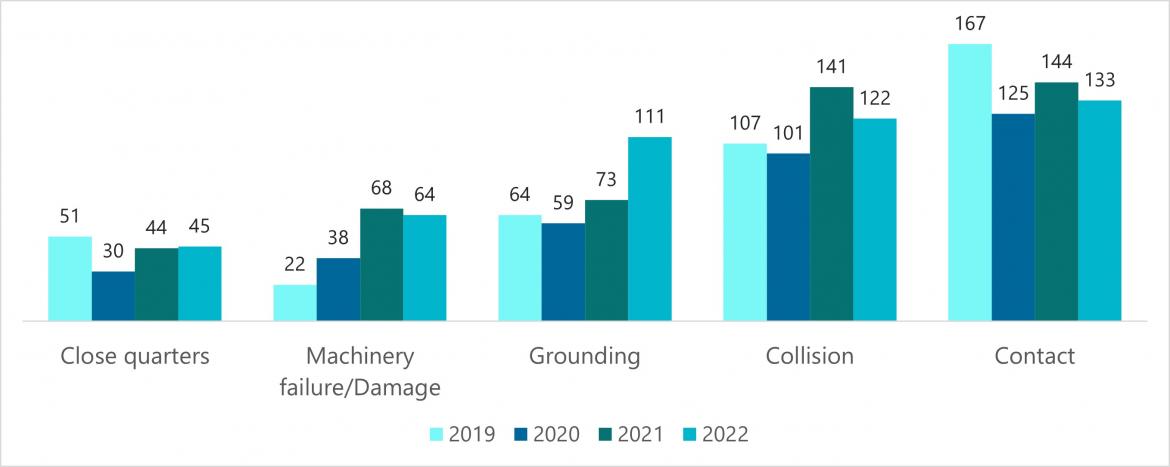
Over half (55.1%) of marine incidents in 2022 included a vessel consequence outcome. The three most frequently occurring consequences on DCVs in 2022 were collisions, groundings and contacts (with something other than a vessel) (Figure 9, Table A5).
In 2022:
- Collisions, groundings and/or contacts accounted for 54.3% (75) of the total very serious and serious (138) incidents involving consequences to a vessel. This represents a 4.3% decrease from the proportion in 2021 (58.6%) (Figure 10).
- Grounding incident reports increased by 52.1% from 2021(Figure 9) and comprised the majority of serious vessel consequences (Figure 10).
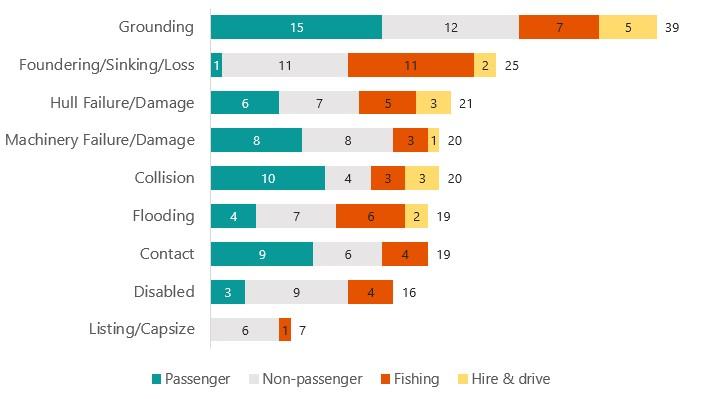
The most frequently reported consequence across all severity levels for each vessel class in 2022 were (Table A5):
- Passenger: Contact (26.0%)
- Non-passenger: Contact (25.2%)
- Fishing: Foundering/sinking/loss (20.5%)
- Hire and drive: Collision (42.3%)
Figure 10 shows the vessel consequence type for very serious and serious incidents by vessel class.
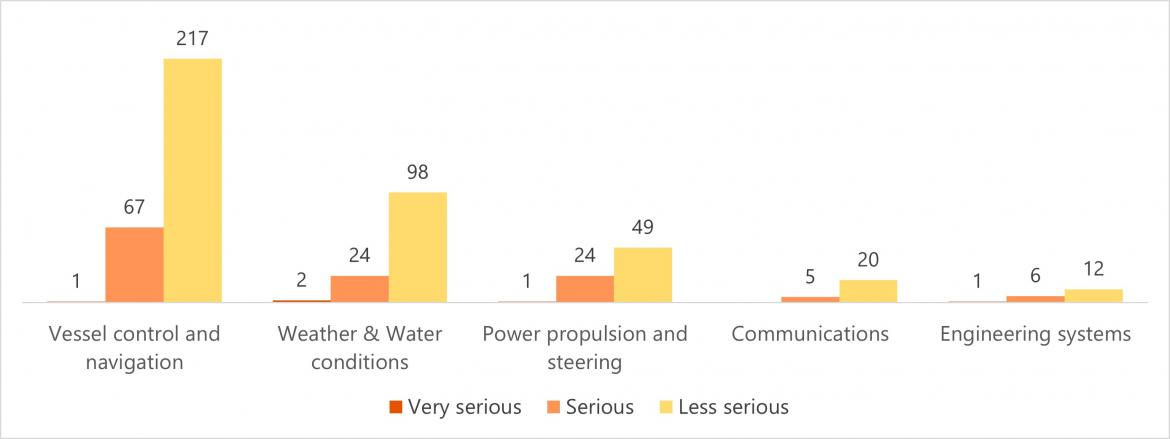
Consistent with crew injury incidents, shortfalls in the control and navigation of a vessel were reported in 46.3% (285) of vessel consequence incidents, followed by 19.6 % (124) for weather/water conditions and 12.7% (74) for power, propulsion and steering failures.
There were 8 very serious DCV incidents in 2022 all involving very serious consequences to the vessel resulting in a total loss or being lost at sea (Table 5).
Vessel type | Consequence/s | Incident circumstances |
Non-passenger | Foundering/Sinking/Loss | Environment: Weather |
Non-passenger | Hull failure/Damage & Foundering/Sinking/Loss | Vessel systems: Mooring / Anchoring |
Non-passenger | Explosion | Engineering systems: Electrical (Batteries) |
Fishing | Foundering/Sinking/Loss Evacuation | Structure: Integrity |
Fishing | Foundering/Sinking/Loss Crew POB (Survived) | Environment: Weather |
Fishing | Fire Machinery/Work Space | Unknown13 |
Hire and drive | Foundering/Sinking/Loss | Maintenance: Enclosed space Vessel systems: Other (Potable water system) |
Hire and drive | Foundering/Sinking/Loss | Power Propulsion and Steering: Steering Gear Vessel Control and Navigation: Vessel Handling/Loss of Control |
Footnotes
13. Vessel lost. Unable to determine seat of fire.