2.1 Location
Kangaroo Island lies off the coast of the state of South Australia, approximately 112 kilometres southwest of Adelaide. As Australia’s third-largest island, Kangaroo Island is a 4,405 square-kilometre landmass that abuts Backstairs Passage and Investigator Strait. Cape St Albans forms the most easterly point of the island and is situated to the south of Backstairs Passage. With Antechamber Bay to the east and Moncrieff Bay to the west, the cape is a narrow neck of land situated within the gazetted locality of Willoughby.
Lighthouse coordinates: 35° 48.2300'S, 138° 07.5120'E
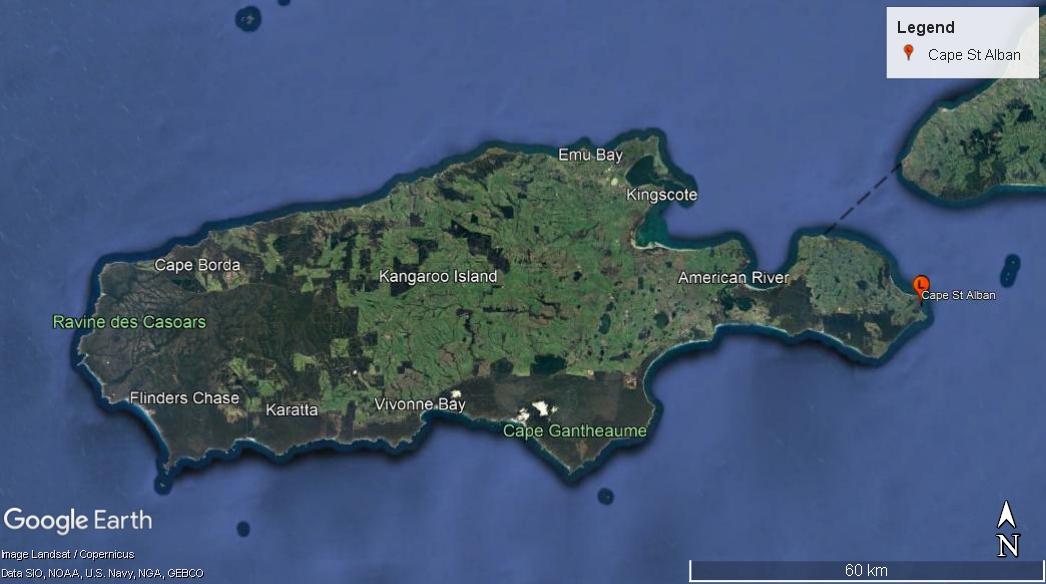 Figure 3. Kangaroo Island with Cape St. Albans Lighthouse on east coast (Image: Landsat/Copernicus, Data: SIO, NOAA, U.S. Navy, NGA, GEBCO)
Figure 3. Kangaroo Island with Cape St. Albans Lighthouse on east coast (Image: Landsat/Copernicus, Data: SIO, NOAA, U.S. Navy, NGA, GEBCO)
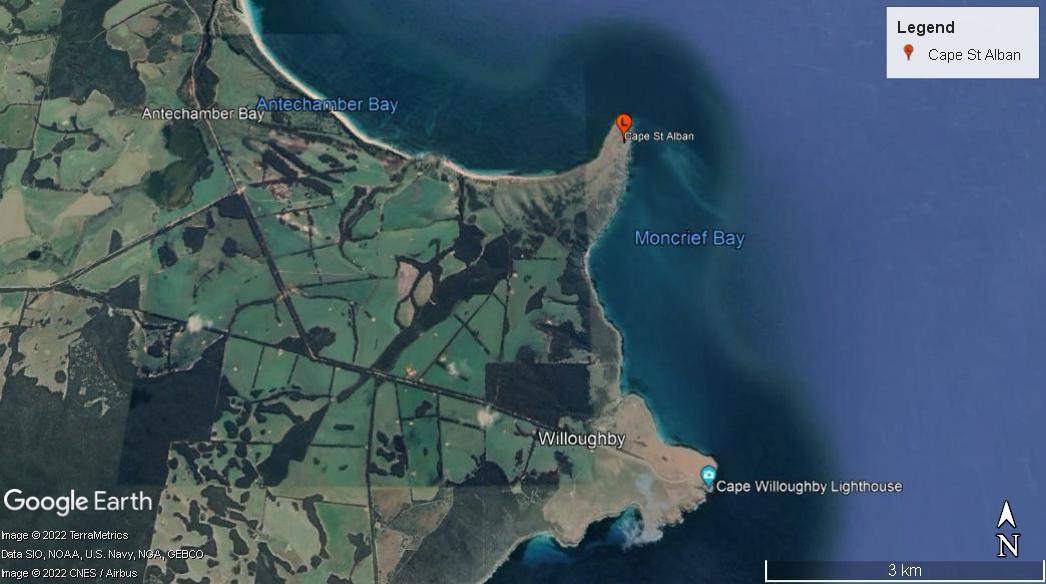 Figure 4. Cape St Alban on eastern coast of Kangaroo Island (Image: ©2022 TerraMetrics, ©2022 CNES/Airbus, Data: SIO, NOAA, U.S Navy, NGA, GEBCO)
Figure 4. Cape St Alban on eastern coast of Kangaroo Island (Image: ©2022 TerraMetrics, ©2022 CNES/Airbus, Data: SIO, NOAA, U.S Navy, NGA, GEBCO)
2.2 Setting and landscape
Cape St. Albans is a relatively bare, flat promontory that forms the most eastern point of Kangaroo Island. Jagged cliffs form the edge of the cape which abuts Backstairs Passage.
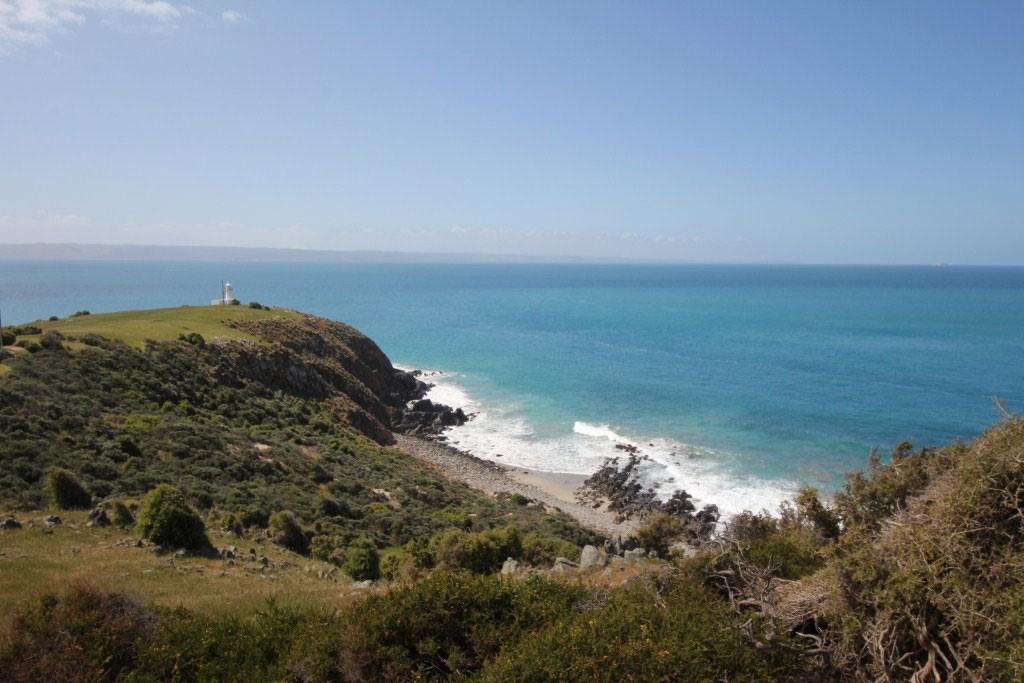 Figure 5. View of Cape St Albans landscape and tower (© AMSA, 2014)
Figure 5. View of Cape St Albans landscape and tower (© AMSA, 2014)
Fauna and flora
A quarter of Kangaroo Island’s landmass is conserved within conservation parks, national parks and wilderness protection areas. The island is also void of pests such as rabbits and foxes due to its isolation.
The following faunal species are native to the island:
- Kangaroo Island western grey kangaroo (macropus fuliginosus fuliginosus)
- Rosenberg’s sand goanna (Varanus rosenbergi)
- Southern brown bandicoot (isoodon obesulus)
- Tammar wallaby (macropus eugenii)
- Common brushtail possum (trichosurus vulpecula)
- Short-beaked echidna (tachyglossus aculeatus)
- Australian sea lion (neophoca cinerea)
- Long-nosed fur seal (arctocephalus forsteri)
The following faunal species have been introduced to the island:
- Koala (phascolarctos cinereus)
- Common ringtail possum (pseudocheirus peregrinus)
- Platypus (Ornithorhynchus anatinus)
The island has also been identified as an Important Bird Area by BirdLife International.5
As of 2012, the waters below Cape St. Albans were included within the Habitat Protection Zone (HPZ) of the Encounter Marine Park Management Plan.6 A HPZ is defined in the Marine Parks Act 2007 as “a zone primarily established so that an area may be managed to provide protection for habitats and biodiversity within a marine park, while allowing activities and uses that do not harm habitats or the functioning of ecosystems”.7
2.3 Lease and ownership
The lighthouse is situated within gazetted Commonwealth land. As the Commonwealth Authority, AMSA manages and maintains the lighthouse.
2.4 Access
Cape St Albans is accessible from Penneshaw via 25 kilometres of sealed roads, unsealed roads and steep rocky track that required a 4WD vehicle. Access to the tower also requires crossing through privately owned gates. Authorised personnel only are permitted access to the site and inside the tower.
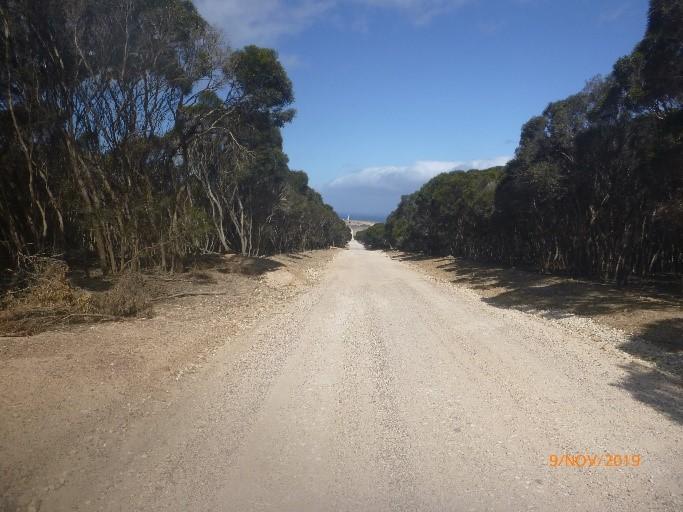 Figure 6. Unsealed road to Cape St Albans Lighthouse (© AMSA, 2019)
Figure 6. Unsealed road to Cape St Albans Lighthouse (© AMSA, 2019)
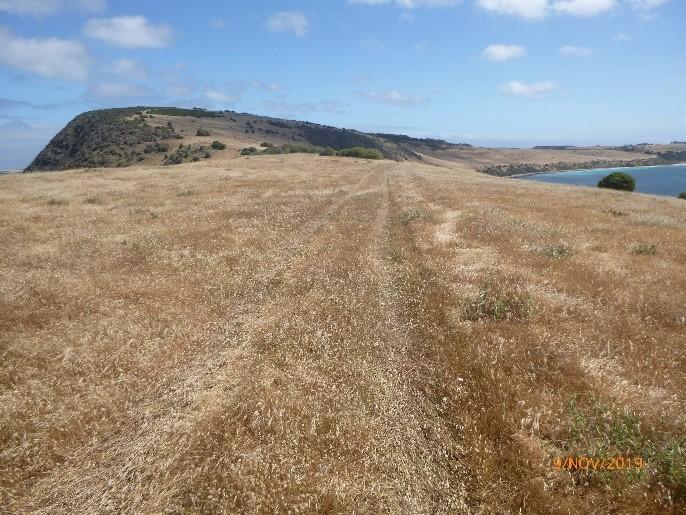 Figure 7. Access track to Cape St Albans Lighthouse (© AMSA, 2019)
Figure 7. Access track to Cape St Albans Lighthouse (© AMSA, 2019)
2.5 Listings
Cape St Albans Lighthouse is listed on the following heritage registers:
| List | ID |
|---|---|
| Commonwealth Heritage List | 1054138 |
| Register of the National Estate | 74269 |
Footnotes
5 ‘Important Bird Areas factsheet: Kangaroo Island’, BirdLife International
6 Department of Environment, Water and Natural Resources, Encounter Marine Park Management Plan 2012, (Government of South Australia, 2012), 14
7 Department of Environment, Water and Natural Resources, Encounter Marine Park Management Plan 2012, 13.
8 ‘Cape St Alban Lighthouse, Cape St Albans Rd, Penneshaw, SA, Australia’, Australian Heritage Database, Commonwealth Heritage List
9 ‘Cape St Alban Lighthouse, Cape St Albans Rd, Penneshaw, SA, Australia’, Australian Heritage Database, Register of the National Estate