The AMSA Response Centre is the main contact for all maritime casualties in Australian waters.
Call 02 6230 6811 or 1800 641 792.
The chances of a vessel in distress, otherwise known as a 'maritime casualty', causing a major risk to Australia’s coastal interests are small, but the potential environmental consequences could be devastating.
This means incidents must be rapidly and effectively addressed.
Part of this response is an ocean-going emergency towage capability to assist with shipping casualties and to prevent pollution.
Although it is always the first responsibility of the ship-owner and operator to seek assistance when an incident occurs, Australia’s state, territory and federal governments recognise the benefits of an integrated emergency response capability.
This means timely support and direction can be provided when and where necessary.
This integrated approach is supported by:
- port authorities
- shipping interests
- other stakeholders.
Emergency towage capability
Emergency towage is an important part of our maritime casualty management capabilities. It is part of the initial response to assist a vessel that is incapacitated and in danger of grounding, sinking or causing pollution.
Emergency towage capability is supported by authorities who manage the risks within their respective jurisdictions. It involves three 3 levels of capability:
- A dedicated emergency towage vessel operating in Far North Queensland and the Torres Strait provided by the vessel Reef Keeper, based in Cairns.
- Contracted port towage around the other major Australian ports capable of undertaking open water towage operations.
- Vessels of opportunity that can be directed or contracted to assist, when required.
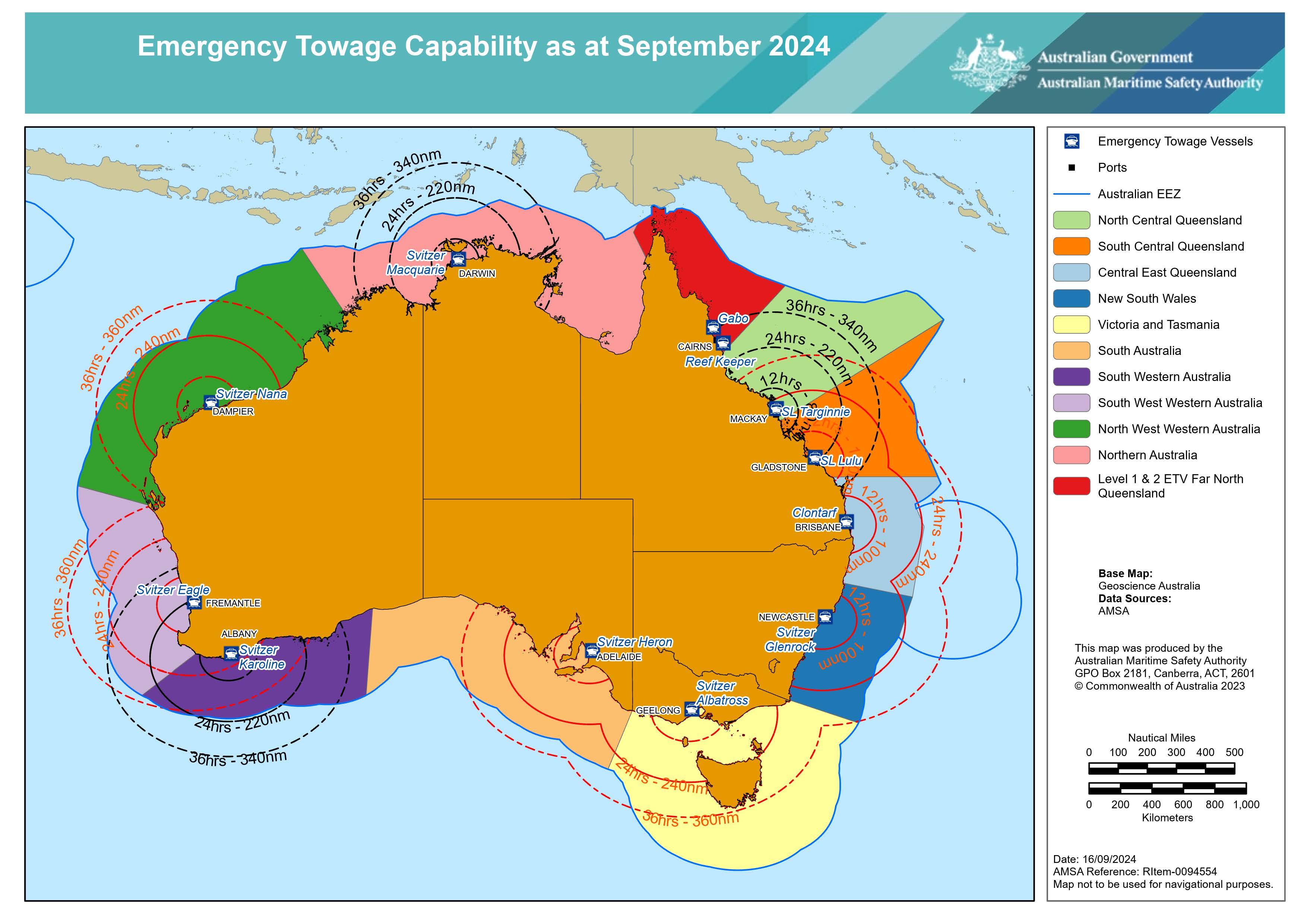
Download the Emergency towage capability map PDF532.56 KB.
Maritime emergency response commander
To ensure fast, decisive action, we have appointed a Maritime Emergency Response Commander (MERCOM).
The MERCOM will act on behalf of the authority during a shipping casualty where there is a risk of significant pollution.
State and Northern Territory governments retain powers to deal with lesser pollution or environmental threats, and may still exercise powers independently.
The MERCOM is also able to take action, but must consider the reasonable views and positions of relevant authorities and stakeholders.
Stakeholders and authorities represent community views about economic, environmental, community and social interests that could be impacted by the MERCOM’s decisions.
Polluter pays
The principles of ‘potential polluter pays’ and ‘polluter pays’ apply where localised pollution or damage results from actions taken to prevent widespread pollution.
In the event of pollution or other damage, the ship requiring assistance pays costs and liabilities.
This is in accordance with the generally applicable principles under international conventions and domestic laws.